Get insight on the state of the global market and key consumer trends.
Euromonitor International recently held a webinar sharing valuable insights into the latest Global Trends in Fresh and Staple Foods. For U.S. suppliers seeking to expand their efforts to export their food and agricultural products internationally, it is vital to understand the fluctuations in the market and consumer preferences. This knowledge can help suppliers choose the appropriate market at the right time for their products.
Fresh and Staple Foods:
This webinar examines trends in both fresh and staple foods. Staple foods generally refer to food items sold to consumers pre-packaged at the point of sale. This includes products such as baked goods, breakfast cereals, processed fruit and vegetables, processed meat and seafood, rice, pasta, and noodles. On the other hand, fresh foods refer to fresh, uncooked, and unprocessed foods, whether packaged or unpacked. This includes products such as eggs, fish and seafood, fruits, vegetables, meat, nuts, pulses, starchy roots, sugar, and sweeteners. Both these categories hold relevance for U.S. suppliers of value-added food and agricultural products, depending on what they manufacture.
State of the Market:
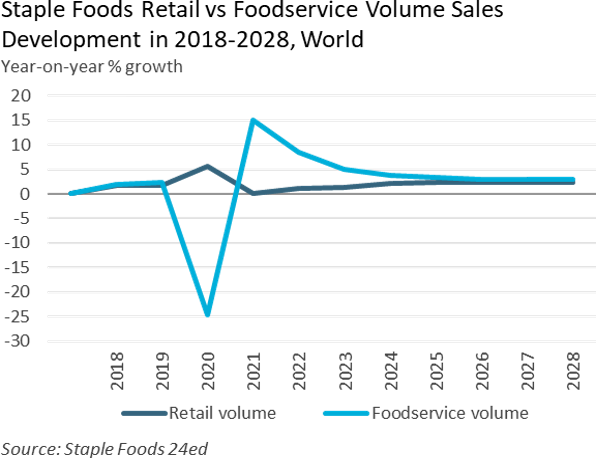
For staple foods, 2023 retail value sales reached US$1.1 trillion worldwide, heavily influenced by the effects of inflation on food prices. In light of price increases, the cost-of-living increases, and the recovery of food service post-pandemic, retail volume sales saw weaker growth, with overall growth of 1.4% worldwide. Developed markets like Western Europe are expected to see a decrease in growth due to these global strains. Still, the U.S. remains the largest market in absolute growth.
In contrast, emerging markets are expected to grow faster, with demand for products like rice, pasta, and noodles increasing as populations grow in the Asia-Pacific region. Among staple foods, baked goods remain the largest category for sales worldwide, accounting for 44% of value and still growing. Processed meat, seafood, and alternatives show weaker growth across all regions as prices increase and more consumers participate in the “away from animals” trend.
The volume of fresh food sales remains virtually unchanged, with rising prices due to supply strains, avian flu, geopolitical conflict, and climate change slowing growth. The February 2024 issue of the Food Export-Midwest and Food Export-Northeast Global Food Marketer provides further insight into some of these trends and how they may affect the operations of U.S. suppliers in 2024.
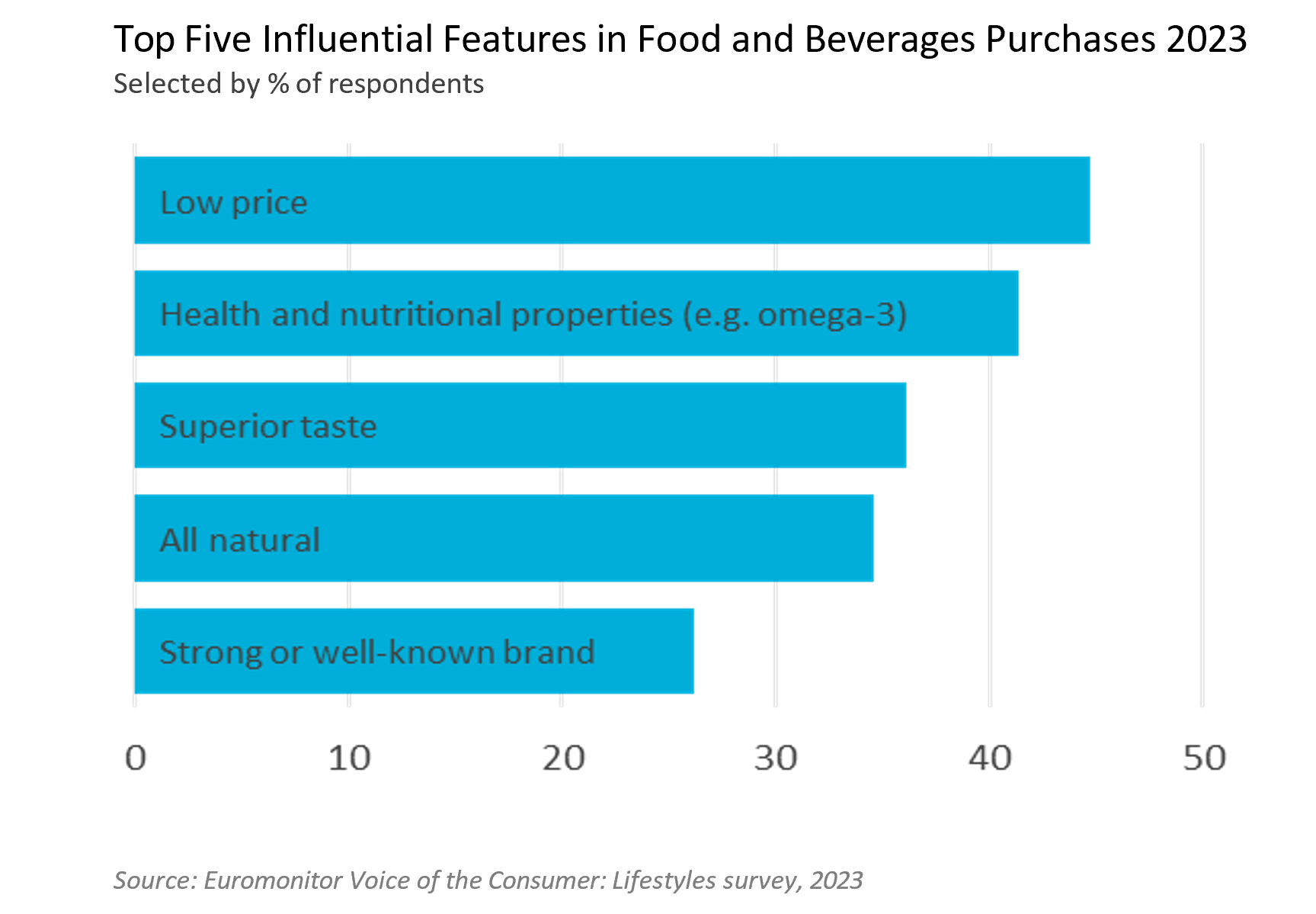
Asia-Pacific dominates the fresh food market, especially in vegetables and fruits. Nuts, vegetables, and fruits see continued growth across countries, with consumers seeking healthier snack options and hoping to guard against illness. India is approaching the top spot for absolute growth in fresh food, though China remains in the lead for the time being. India became the most populous country in the world in 2023, with a population of 1.42 billion.
Top Trends Shaping Industries:
Convenience remains a strong motivator for food choices. With more people returning to work, they have less time and energy to devote to cooking. According to two Voice of the Consumer surveys, 38.2% of European consumers are willing to spend extra money to save time, and 43.5% of U.S. consumers reheat/prepare a ready meal at least one to two times per week.

These evolving mentalities have led to the development of new convenient food options, such as the Adriana eco-friendly pasta in the Czech Republic. This pasta can be cooked directly within the sauce, saving time and energy.
Similarly, Nissin Cup Noodles collaborated with seasonal pop-up bars in the U.S. to elevate the instant food experience with beer and instant noodle pairings. Amidst global uncertainties, premiumization and customization can help consumers visualize these foods as more than just a “broke” meal.
Climate change remains a persistent threat, with erratic weather patterns expected to disrupt agricultural harvests worldwide in the coming years. Climate change’s unpredictability is increasing consumer demand for ethical sourcing, sustainable products, and transparent labeling. Companies are changing practices to enable consumers to make climate-conscious choices, such as introducing carbon-neutral products. As consumer concerns surrounding health and the environment rise, government regulations on packaging start to tighten. It has been anticipated that the FDA will introduce a restriction on the word “healthy” – any packing using this term must now contain food such as fruit, vegetables, or dairy, and must fall within the limits for saturated fat, sodium, and added sugar.
Key Takeaways:
Conclusion:
The data provided by Euromonitor International helps organizations like Food Export-Midwest and Food Export-Northeast dissect the emerging trends in the global food market, shaped by evolving consumer preferences, economic fluctuations, and environmental challenges. Staying informed of these trends is vital for strategic decision-making and successful penetration of international markets for U.S. suppliers. As the industry navigates uncertainties, embracing innovation and sustainability will be key in driving long-term growth.
Your Connection To Growth®
©2024 Food Export Association of the Midwest USA and Food Export USA–Northeast. All Rights Reserved.
Food Export–Midwest and Food Export–Northeast prohibits discrimination in all its programs and activities on the basis of race, color, national origin, religion, sex, gender identity (including gender expression), sexual orientation, disability, age, marital status, familial/parental status, income derived from a public assistance program, political beliefs, reprisal or retaliation for prior civil rights activity. (Not all bases apply to all programs.) Persons with disabilities who require reasonable accommodations or alternative means of communication for program information (e.g., Braille, large print, audiotape, American Sign Language, etc.) should contact us. Additionally, program information may be made available in languages other than English.
To file a program discrimination complaint, complete the USDA Program Discrimination Complaint Form, AD-3027, found online https://www.ascr.usda.gov/filing-program-discrimination-complaint-usda-customer.
Food Export–Midwest and Food Export–Northeast reserve the right to deny services to any firm or individual which, in the sole opinion of Food Export–Midwest and Food Export–Northeast, does not comply with FAS, MAP or Food Export–Midwest and Food Export–Northeast regulations or policies, or otherwise offer the best opportunity to achieve its mission of increasing food and agricultural exports. Submission of any false or misleading information may be grounds for rejection or subsequent revocation of any application or participation. Food Export–Midwest and Food Export–Northeast are equal opportunity employers and providers.
